As viruses are obligate intracellular pathogens they cannot replicate without the machinery and metabolism of a host cell. Though the details of virus infection and replication vary greatly with host type all viruses share 6 basic steps in their replication cycles.
Intro To Viruses Article Viruses Khan Academy
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.

. Besides this the cell membrane also protects the cellular component from damage and leakage. However bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria have a unique shape with a geometric head and filamentous tail fibers. The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell.
This is called the lysogenic. Viruses generally come in two forms. The capsid shape varies from simple helical and icosahedra forms to more complex structures with tails.
Successfully structuring an essay means attending to a readers logic. The capsid and entire virus structure can be mechanically physically probed through atomic force microscopy. In general there are five main morphological virus types.
The genetic material or genome of a virus may consist of single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA and may be linear or circular in form. Helical viruses have an elongated tube-like structure with the. Some viruses are also enclosed by an envelope of fat and protein molecules.
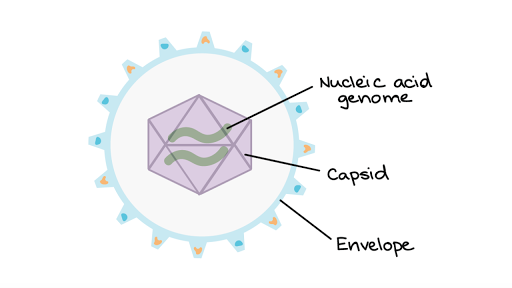
This arrangement results in virions which. Structure of Viruses. A virus particle consists of DNA or RNA within a protective protein coat called a capsid.
As shown in the virus must first attach itself to the host cell. The virion capsid has three functions. No matter the shape all viruses consist of genetic material DNA or RNA and have an outer protein shell known as a capsid.
Viruses are small. The infectious external covering core of a virus is called the virion. Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites and are completely dependent upon the cell for replication.
The parental virus virion gives rise to numerous progeny usually genetically and structurally identical to the parent virus. All viruses contain nucleic acid either DNA or RNA but not both and a protein coat which encases the nucleic acid. The typical structure of a virion which is the term used to describe a single virus includes an outer shell that is otherwise referred to as the protein capsid or membrane.
Because it is a. What is the structure and genome of a typical plant virus. STRUCTURE OF A VIRUS Viruses contain nucleic acideither DNA deoxyribonucleic acid or RNA ribonucleic acid and protein.
Helical viruses have an elongated tube-like structure with the capsomers arranged helically around the coiled genome. Some scientists speculate that viruses started as rogue segments of genetic code that adapted to a parasitic existence. What a virus is.
Although the replicative life cycle of viruses differs greatly between species and category of virus there are six basic stages that are essential for viral replication. In the vegetative cycle of viral infection multiplication of progeny viruses can be. Helical These viruses are composed of a single type of capsomere stacked around a central axis to form a helical structure which may have a central cavity or tube.
Because essays are essentially linearthey offer one idea at a timethey must present their ideas in the order that makes most sense to a reader. A typical bacterium is 23 μM in. Although relatively simple viruses exhibit significant diversity in terms of size genome organization and capsid architecture.
Viral proteins on the capsid or phospholipid envelope interact with. Viral nucleocapsids come in two basic shapes although the overall appearance of a virus can be altered by the presence of an envelope if present. Viruses are infectious agents that are not cellular in nature.
The meaning of VIRUS is any of a large group of submicroscopic infectious agents that are usually regarded as nonliving extremely complex molecules that typically contain a protein coat surrounding an RNA or DNA core of genetic material but no semipermeable membrane that are capable of growth and multiplication only in living cells and that cause various important. Summary of Key Concepts. The shape of the capsid may vary from one type of virus to another.
The actions of the virus depend both on its destructive tendencies toward a specific host cell and on environmental conditions. The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell. Unlike the growth curve for a bacterial population the growth curve for a virus population over its life cycle does not follow a sigmoidal curve.
Viral nucleocapsids come in two basic shapes although the overall appearance of a virus can be altered by the presence of an envelope if present. Most viruses are in the range of 20200 nm although some viruses can exceed 1000 nm in length. Viruses vary in their structure.
It forms the wall-like structure between two cells as well as between the cell and its surroundings. A typical virus consists of a protective protein coat known as a capsid. During the initial stage an inoculum of virus causes infection.
Describe the replication process of animal viruses. The nucleic acid encodes the genetic information which is unique for each virus. Writing an academic essay means fashioning a coherent set of ideas into an argument.
They consist of a nucleic acid genome packaged within a protein shell. Other types of virus called phages either join their DNA to that of their host or leave small circles of their DNA in the cytoplasm of their host cell or cells. By structure it is a porous membrane with pores which permit the movement of selective substances in and out of the cell.
The capsid is made from the proteins that are encoded by viral genes within their genome. Scientists use the word novel to distinguish the new form of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 currently making people sick from previous types of coronaviruses such as SARS and MERS. Viruses can reproduce only within a host cell.
A virus particle is made up of genetic material housed inside a protein shell or capsid.

Virus Definition Structure Classification Examples Biology Dictionary

Virus Definition Structure Classification Examples Biology Dictionary

0 Comments